The making of the fittest natural selection and adaptation answers – Embarking on an exploration of the making of the fittest, this discourse delves into the mechanisms of natural selection and adaptation, unraveling their profound impact on the evolutionary journey. As we delve into the intricacies of these processes, we uncover the selective pressures that shape the survival and proliferation of organisms, ultimately leading to the emergence of the fittest.
Natural selection, the driving force behind evolution, favors individuals with advantageous traits, granting them a competitive edge in the relentless struggle for survival. Adaptation, a testament to the resilience of life, equips organisms with specialized characteristics that enhance their fitness within diverse environments.
Together, these forces orchestrate the making of the fittest, shaping the tapestry of life on Earth.
1. The Mechanisms of Natural Selection
Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism of evolution that drives the survival and reproduction of organisms with advantageous traits. It acts on heritable variations within a population, leading to the accumulation of favorable alleles and the gradual adaptation of species to their environment.
Natural selection occurs when individuals with certain traits have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing in a particular environment compared to those without those traits. These advantageous traits, such as better camouflage or more efficient metabolism, provide a survival and reproductive advantage, allowing individuals with those traits to pass on their genes to the next generation more frequently.
Over time, the frequency of favorable alleles in a population increases as individuals with those alleles have a higher chance of survival and reproduction. This process leads to the gradual adaptation of a population to its environment, as the traits that enhance survival and reproduction become more common within the population.
Genetic Basis of Natural Selection
Natural selection operates on the genetic variation present within a population. This variation arises from mutations, genetic recombination, and other mechanisms that introduce changes in the genetic makeup of individuals.
When natural selection favors certain traits, the alleles that code for those traits become more common in the population. This is because individuals with those alleles have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing, passing on their favorable genes to the next generation.
Over time, the accumulation of favorable alleles in a population leads to the adaptation of the population to its environment. This process can result in the evolution of new species or the divergence of populations into distinct lineages.
2. The Role of Adaptation in Evolution
Adaptation is a trait or characteristic that enhances the survival and reproductive success of an organism in its specific environment. Adaptations arise through natural selection, as individuals with advantageous traits have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing.
Adaptations can take many forms, such as physical structures, physiological processes, or behavioral patterns. For example, the long necks of giraffes allow them to reach high into trees for food, while the thick fur of polar bears provides insulation in cold environments.
Adaptations are crucial for the survival and success of species. They allow organisms to exploit specific niches in their environment, avoid predators, and secure resources necessary for survival and reproduction.
Mechanisms of Adaptation, The making of the fittest natural selection and adaptation answers
Adaptations arise through a combination of natural selection and genetic variation. Natural selection favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproduction, while genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
Over time, beneficial traits become more common in a population as individuals with those traits have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing. This process leads to the gradual adaptation of a population to its environment.
Adaptations can also arise through genetic drift, which is the random change in allele frequencies within a population. In small populations, genetic drift can lead to the fixation of certain alleles, including those that may confer an adaptive advantage.
3. The Process of Making the Fittest: The Making Of The Fittest Natural Selection And Adaptation Answers
The process of making the fittest is driven by natural selection and adaptation. Natural selection acts on genetic variation within a population, favoring individuals with advantageous traits that enhance their survival and reproduction.
Selective pressures, such as competition for resources, predation, and environmental factors, influence the survival and reproduction of organisms. Individuals with traits that provide an advantage in a particular environment have a higher chance of surviving and passing on their genes.
Genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon. Mutations, genetic recombination, and other mechanisms introduce changes in the genetic makeup of individuals, creating a diverse range of traits within a population.
Selective Pressures
Selective pressures are environmental factors that influence the survival and reproduction of organisms. These pressures can include:
- Competition for resources such as food, water, and shelter
- Predation and the need to avoid being eaten
- Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light availability
Selective pressures vary across different environments and can change over time. As selective pressures change, so too can the traits that are favored by natural selection.
4. Examples of Natural Selection and Adaptation in Action

Numerous examples demonstrate the power of natural selection and adaptation in shaping the diversity of life on Earth. Here are a few notable cases:
- Peppered moths:During the Industrial Revolution, soot pollution darkened tree trunks in England, making light-colored peppered moths more vulnerable to predation by birds. As a result, dark-colored moths became more common through natural selection, demonstrating how environmental changes can drive adaptation.
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria:When exposed to antibiotics, some bacteria develop mutations that confer resistance. These resistant bacteria have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing, leading to the spread of antibiotic resistance within bacterial populations.
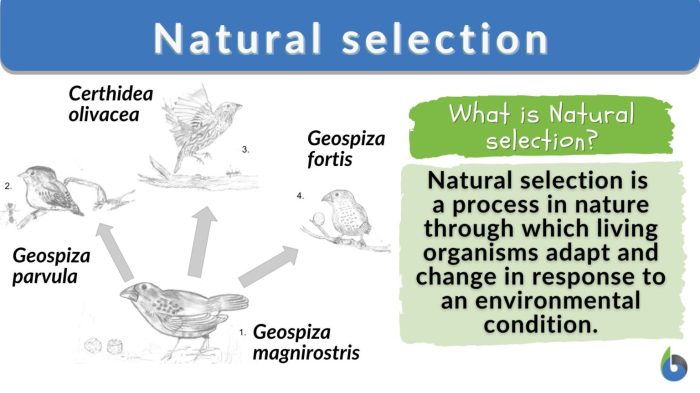
- Beak size in finches:Charles Darwin’s observations of finches on the Galapagos Islands revealed that different species had beaks adapted to specific food sources. Natural selection favored beaks that were best suited for obtaining food in each environment.
These examples illustrate how natural selection and adaptation drive the evolution of traits that enhance the survival and reproduction of organisms in their specific environments.
Clarifying Questions
What is the fundamental principle of natural selection?
Natural selection favors individuals with advantageous traits, increasing their chances of survival and reproduction.
How do adaptations contribute to the fitness of organisms?
Adaptations enhance the survival and reproductive success of organisms by providing specialized characteristics that suit specific environments.
What is the role of genetic variation in natural selection?
Genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, creating a diverse pool of traits within populations.
