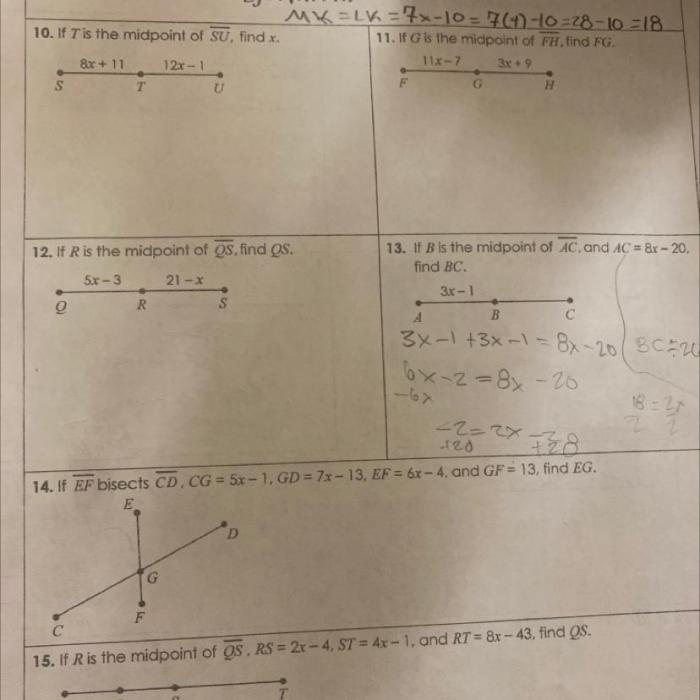
Unit 1 geometry basics homework 2 segment addition postulate – In geometry, the Segment Addition Postulate is a fundamental principle that establishes the relationship between the lengths of segments on a line. This postulate serves as a cornerstone for various geometric proofs and applications, providing a solid foundation for understanding and solving geometry problems.
The Segment Addition Postulate states that if a point C lies between points A and B on a line, then the distance from A to B is equal to the sum of the distances from A to C and from C to B.
Mathematically, this can be represented as AB = AC + CB.
Segment Addition Postulate

The Segment Addition Postulate states that if point B is between points A and C, then AB + BC = AC.
Explanation, Unit 1 geometry basics homework 2 segment addition postulate
This postulate is fundamental in geometry and has numerous applications in problem-solving and proving theorems. It establishes the relationship between the lengths of segments on a line and allows for the calculation of unknown segment lengths.
Applying the Postulate to Solve Problems
| Given | Postulate Applied | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| AB = 5 cm, BC = 3 cm | AB + BC = AC | AC = 5 cm + 3 cm = 8 cm |
| AC = 12 cm, AB = x | AB + BC = AC | BC = AC
|
Proving the Postulate
The Segment Addition Postulate can be proven using a geometric construction. Draw a line segment AC and mark point B between A and C. Construct rays from B to A and C, forming the triangles ABM and BCM. By the Triangle Inequality Theorem, AB + BC > BM and BC + AC > CM.
Since BM = CM, we have AB + BC > CM and BC + AC > CM. Therefore, AB + BC = AC.
Related Concepts and Theorems
- Distance Formula: The Distance Formula is an extension of the Segment Addition Postulate and is used to calculate the distance between two points in a coordinate plane.
- Midpoint Theorem: The Midpoint Theorem states that the midpoint of a line segment divides the segment into two equal parts, and its proof relies on the Segment Addition Postulate.
Examples and Applications
The Segment Addition Postulate is used in various practical applications, such as:
- Architecture: Determining the total length of a building or structure by adding the lengths of its individual segments.
- Engineering: Calculating the distance between two points on a map or blueprint by measuring the lengths of the segments connecting them.
FAQ Overview: Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 2 Segment Addition Postulate
What is the Segment Addition Postulate?
The Segment Addition Postulate states that if a point C lies between points A and B on a line, then the distance from A to B is equal to the sum of the distances from A to C and from C to B.
How is the Segment Addition Postulate used in geometry?
The Segment Addition Postulate is used to determine the lengths of segments, construct geometric figures, and solve a wide range of geometry problems.
What is the mathematical representation of the Segment Addition Postulate?
The mathematical representation of the Segment Addition Postulate is AB = AC + CB, where A, B, and C are points on a line and AB represents the distance from A to B.