All of the following are autoimmune diseases except… This intriguing question opens the door to a captivating exploration of the complexities of autoimmune diseases, their mechanisms, and the exceptions that challenge our understanding. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of the immune system, unraveling the mysteries of autoimmune disorders and discovering the nuances that set them apart.
Autoimmune diseases arise when the body’s immune system, designed to protect against foreign invaders, mistakenly turns against its own healthy cells. This misdirected attack can lead to a wide range of symptoms and conditions, affecting various organs and tissues throughout the body.
Understanding the mechanisms behind autoimmune diseases is crucial for developing effective diagnostic and treatment strategies.
Common Autoimmune Diseases
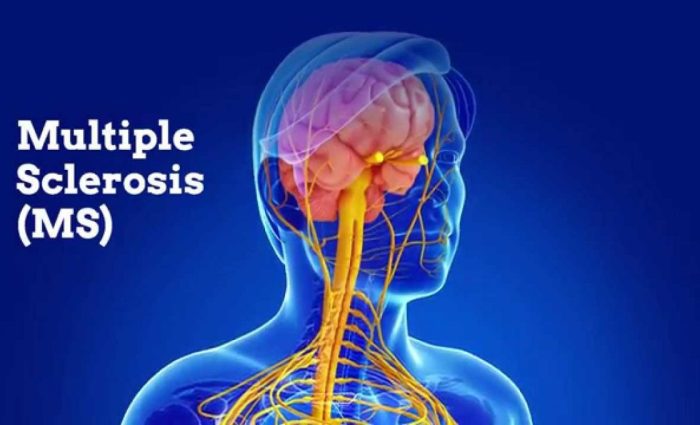
Autoimmune diseases are a group of conditions in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues. Common autoimmune diseases include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Lupus: A systemic disease that can affect multiple organs, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and heart.
- Multiple sclerosis: Affects the central nervous system, causing muscle weakness, numbness, and vision problems.
- Celiac disease: An intolerance to gluten that damages the small intestine.
- Type 1 diabetes: An autoimmune disease that affects the pancreas, leading to an inability to produce insulin.
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: An autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland, causing an underproduction of thyroid hormones.
- Graves’ disease: An autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland, causing an overproduction of thyroid hormones.
Exceptions to Autoimmune Diseases
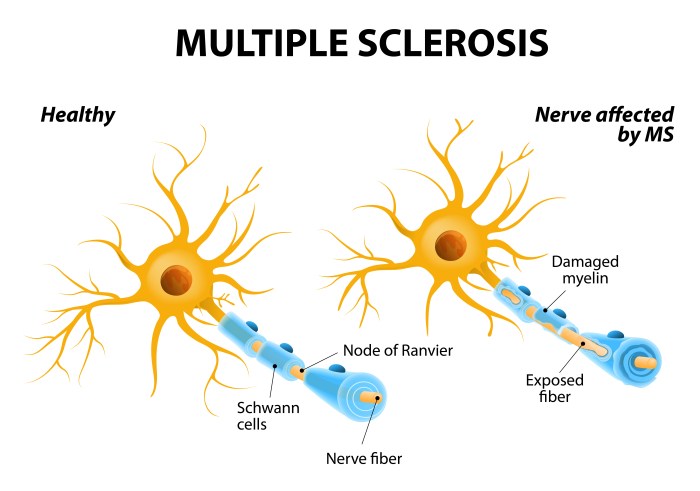
Cancer is not an autoimmune disease. Cancer is a condition in which cells grow out of control and form tumors. It is not caused by the immune system attacking healthy tissues.
Autoimmune Disease Mechanisms
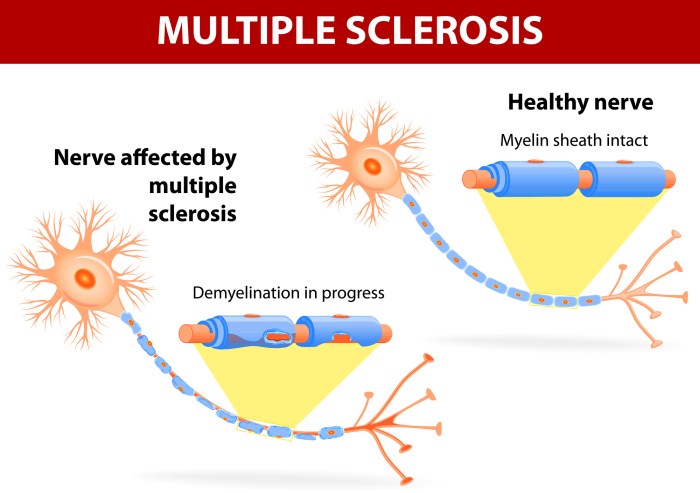
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly identifies healthy cells as foreign and launches an attack against them. This process involves:
- Loss of tolerance: The immune system normally learns to recognize and tolerate self-antigens, which are molecules present on the body’s own cells.
- Activation of autoreactive lymphocytes: Autoreactive lymphocytes are immune cells that mistakenly recognize self-antigens as foreign.
- Production of autoantibodies: Autoreactive lymphocytes produce autoantibodies, which are antibodies that bind to self-antigens and trigger an immune response.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases: All Of The Following Are Autoimmune Diseases Except
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases involves:
- Physical examination and medical history
- Blood tests to detect autoantibodies
- Imaging tests to assess organ damage
Treatment options for autoimmune diseases include:
- Immunosuppressive drugs: These drugs suppress the immune system to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage.
- Biologic therapies: These drugs target specific molecules involved in the immune response.
- Lifestyle modifications: Some autoimmune diseases can be managed with lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise.
Impact of Autoimmune Diseases
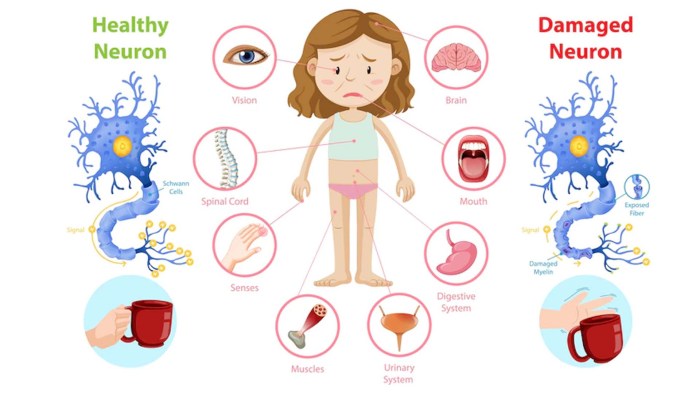
Autoimmune diseases can have a significant impact on individuals and society. They can cause:
- Chronic pain and disability
- Organ damage and failure
- Reduced quality of life
- Increased healthcare costs
Research and treatment for autoimmune diseases are ongoing, with the goal of improving patient outcomes and reducing the impact of these conditions.
Quick FAQs
What are the most common autoimmune diseases?
Common autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and Crohn’s disease.
What is the difference between an autoimmune disease and an infection?
Autoimmune diseases are caused by the body’s immune system attacking its own tissues, while infections are caused by external pathogens such as bacteria or viruses.
Can autoimmune diseases be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for autoimmune diseases, but treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.