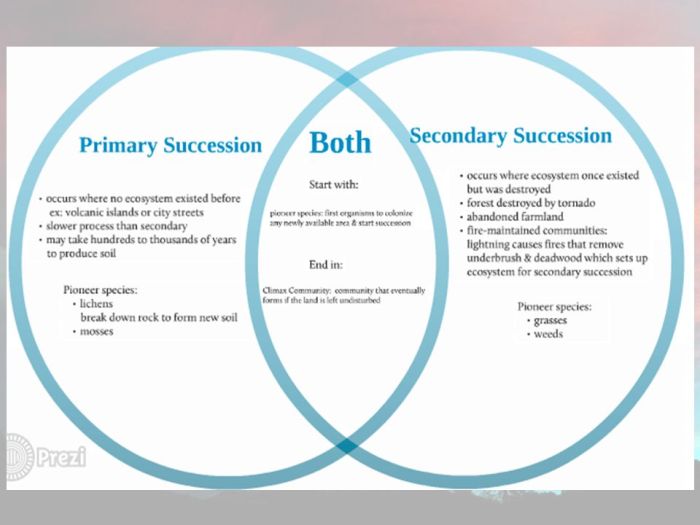
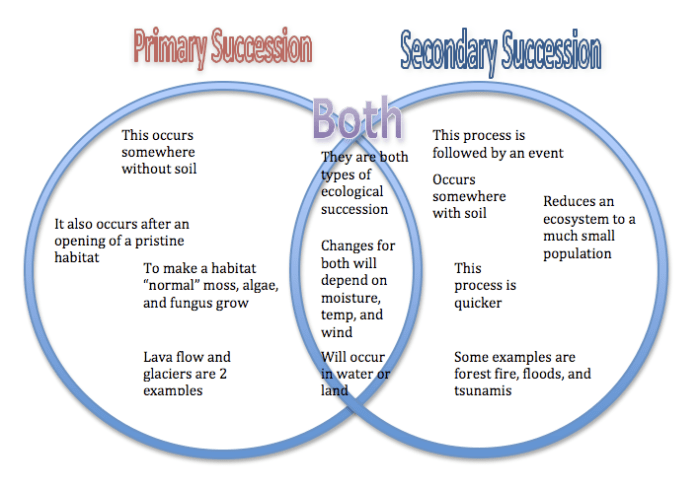
In the realm of ecology, the Venn diagram of primary and secondary succession unravels the intriguing interplay between two fundamental processes that shape ecosystems. Primary succession, the pioneer of new landscapes, and secondary succession, the catalyst for restoration, share common threads while carving unique paths.
Primary succession initiates on barren substrates, devoid of life, while secondary succession takes hold in areas disturbed by natural or human-induced events. As these processes unfold, they leave behind a mosaic of ecological communities, each with its own story to tell.
Venn Diagram of Primary and Secondary Succession
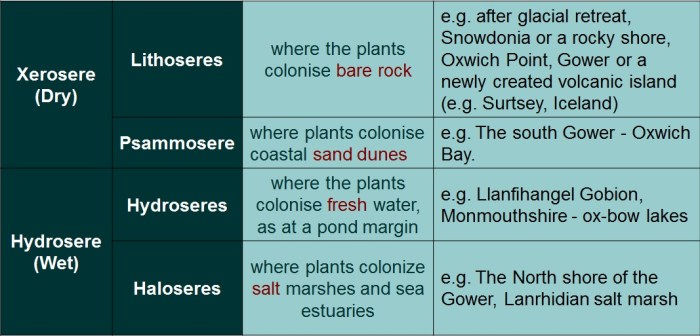
Succession is the gradual change in the species composition of a community over time. Primary succession occurs on newly exposed or created surfaces, such as bare rock, sand, or lava flows. Secondary succession occurs on sites that have been previously disturbed, such as abandoned fields or burned forests.
The following Venn diagram illustrates the similarities and differences between primary and secondary succession:

As shown in the diagram, both primary and secondary succession involve the establishment of new plant communities over time. However, there are also some key differences between the two types of succession.
Factors Influencing Primary and Secondary Succession
Primary succession is influenced by a number of factors, including the type of substrate, the climate, and the availability of propagules. Secondary succession is influenced by a number of factors, including the type of disturbance, the severity of the disturbance, and the availability of propagules.
The following table compares the factors that influence primary and secondary succession:
| Factor | Primary Succession | Secondary Succession |
|---|---|---|
| Type of substrate | Bare rock, sand, or lava flows | Abandoned fields or burned forests |
| Climate | Plays a major role in determining the types of plants that can establish | Plays a less important role than in primary succession |
| Availability of propagules | Limited availability of propagules | Greater availability of propagules |
| Type of disturbance | N/A | Natural disturbances (e.g., fires, floods, hurricanes) or human disturbances (e.g., logging, agriculture) |
| Severity of disturbance | N/A | Can influence the rate and trajectory of succession |
Ecological Significance of Primary and Secondary Succession, Venn diagram of primary and secondary succession
Primary succession is important because it creates new habitats for plants and animals. Secondary succession is important because it helps to restore disturbed ecosystems to their original state.
The following table compares the ecological significance of primary and secondary succession:
| Ecological Significance | Primary Succession | Secondary Succession |
|---|---|---|
| Creates new habitats | Yes | No |
| Restores disturbed ecosystems | No | Yes |
| Provides food and shelter for wildlife | Yes | Yes |
| Improves water quality | Yes | Yes |
| Reduces erosion | Yes | Yes |
Examples of Primary and Secondary Succession
Examples of primary succession include the colonization of bare rock by lichens and mosses, the establishment of plants on sand dunes, and the growth of forests on lava flows.
Examples of secondary succession include the regrowth of forests after a fire, the recovery of grasslands after grazing, and the restoration of wetlands after drainage.
The following table provides a more detailed list of examples of primary and secondary succession:
| Type of Succession | Examples |
|---|---|
| Primary Succession |
|
| Secondary Succession |
|
Frequently Asked Questions: Venn Diagram Of Primary And Secondary Succession
What are the key differences between primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession occurs on barren substrates, while secondary succession occurs in areas that have been disturbed. Primary succession is a slower process, as it involves the establishment of new soil and plant communities, while secondary succession is faster, as it builds on existing soil and plant communities.
What are some examples of primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession can be observed on newly exposed rock surfaces, such as after a volcanic eruption or glacier retreat. Secondary succession can be observed in abandoned fields, burned forests, and areas that have been cleared for development.
What is the ecological significance of primary and secondary succession?
Primary and secondary succession are essential processes for the development and maintenance of ecosystems. They create new habitats, increase biodiversity, and provide food and shelter for wildlife.