Embark on an enthralling exploration with our comprehensive prokaryote and eukaryote POGIL answers, meticulously crafted to unravel the complexities of cellular life. Discover the fundamental differences and striking similarities between these two cell types, shaping the very fabric of biological systems.
Delve into the intricate structures and diverse functions of prokaryotes and eukaryotes, unraveling their evolutionary origins and ecological significance. Prepare to be captivated as we dissect the processes of cell division, tracing the remarkable journeys of these microscopic marvels.
Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cell Structures: Prokaryote And Eukaryote Pogil Answers
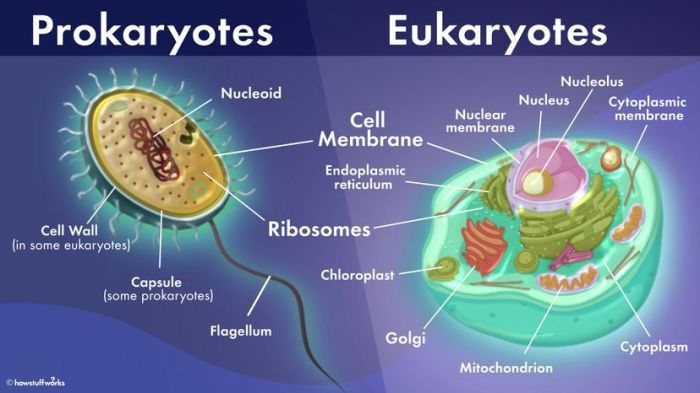
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells exhibit distinct structural features that reflect their diverse roles and evolutionary origins. The following table summarizes the presence or absence of key cell structures in each cell type:
| Cell Structure | Prokaryote | Eukaryote |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Nucleolus | Absent | Present |
| Nuclear Envelope | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Golgi Apparatus | Absent | Present |
| Lysosomes | Absent | Present |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Present in some | Present in plant cells |
| Flagella | Present in some | Present in some |
| Pili | Present in some | Absent |
Functions of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes play vital roles in various ecosystems. Prokaryotes, being the oldest and most abundant organisms on Earth, contribute significantly to:
- Nutrient cycling: Bacteria decompose organic matter and recycle essential nutrients back into the environment.
- Photosynthesis: Cyanobacteria, a type of prokaryote, are responsible for a significant portion of global oxygen production.
- Symbiotic relationships: Prokaryotes form symbiotic relationships with plants, animals, and other organisms, providing mutual benefits.
Eukaryotes, on the other hand, encompass a vast diversity of organisms with specialized functions. Examples include:
- Plants: As primary producers, plants convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, providing the foundation for most food chains.
- Animals: Animals consume plants and other organisms, playing crucial roles in nutrient cycling and maintaining ecosystem balance.
- Fungi: Fungi decompose organic matter and recycle nutrients, contributing to soil fertility and nutrient cycling.
Evolution of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
The evolution of prokaryotes and eukaryotes is a fascinating tale that spans billions of years. Prokaryotes emerged as the first cellular life forms approximately 3.5 billion years ago. Over time, a major evolutionary milestone occurred with the development of eukaryotic cells, which likely arose through endosymbiosis.
Endosymbiosis is the process by which one cell engulfs another, forming a symbiotic relationship. In the case of eukaryotic cells, it is believed that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by a larger host cell. This symbiotic partnership provided the host cell with the ability to generate energy and produce food, leading to the evolution of more complex and efficient eukaryotic cells.
Similarities and Differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
- Similarities:
- Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes are cells that contain genetic material, ribosomes, and a cell membrane.
- Both can be unicellular or multicellular.
- Both use ATP as an energy source.
- Differences:
- Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes have a nucleus and an array of membrane-bound organelles.
- Prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller (70S) than eukaryotic ribosomes (80S).
- Prokaryotes typically have a single, circular chromosome, while eukaryotes have multiple, linear chromosomes.
- Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission, while eukaryotes reproduce through mitosis or meiosis.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Division
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes employ distinct mechanisms for cell division. Prokaryotes undergo binary fission, a simple process in which the cell replicates its chromosome and then divides into two identical daughter cells.
Eukaryotes, on the other hand, undergo mitosis, a more complex process that involves the formation of mitotic spindles, chromosome alignment, and cytokinesis. Mitosis ensures the equal distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.
FAQ Insights
What is the key difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes possess both.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission, a simple process of cell division.
What is the role of eukaryotes in ecosystems?
Eukaryotes play diverse roles, including photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, and decomposition.
