An athlete’s arousal level refers to their physiological and psychological state of readiness for physical activity. Understanding this concept is crucial for optimizing performance, preventing burnout, and managing stress. This article delves into the factors that influence arousal levels, the methods used to measure them, and their applications in athletic training and competition.
Physiological Factors Affecting Arousal Levels
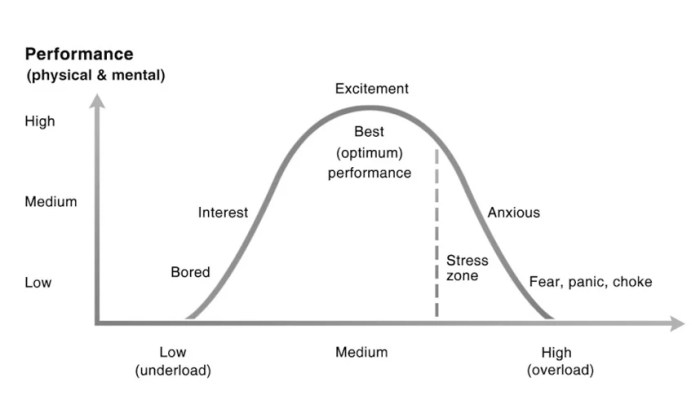
Arousal levels are influenced by a range of physiological factors, including hormonal and nervous system activity.Hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol play a significant role in regulating arousal. Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is released in response to stress and triggers the “fight or flight” response, increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration.
Cortisol, a steroid hormone, is released in response to prolonged stress and helps the body cope with the effects of stress.The nervous system also plays a crucial role in regulating arousal levels. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is responsible for activating the body’s “fight or flight” response, while the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) is responsible for calming the body down.
The SNS and PNS work together to maintain a balance in arousal levels.Physiological changes that occur during different arousal states include changes in heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and muscle tension. In high arousal states, such as during intense exercise or competition, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration increase, while muscle tension increases.
In low arousal states, such as during sleep or relaxation, heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration decrease, while muscle tension decreases.
Psychological Factors Affecting Arousal Levels

Psychological factors play a significant role in influencing an athlete’s arousal levels. These factors include motivation, expectations, anxiety, stress, and cognitive processes.
Influence of Motivation and Expectations
Motivation, or the desire to achieve a goal, can positively affect arousal levels. Athletes who are highly motivated tend to have higher arousal levels, which can enhance their performance. Similarly, athletes with positive expectations about their performance often experience higher arousal levels, as they are confident in their abilities.
Effects of Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress can negatively impact arousal levels. When athletes experience high levels of anxiety or stress, their arousal levels can become too high, which can interfere with their performance. This is because anxiety and stress can lead to muscle tension, increased heart rate, and impaired concentration.
Cognitive Processes
Cognitive processes, such as attention and concentration, can also affect arousal levels. Athletes who are able to focus and concentrate on the task at hand are more likely to have optimal arousal levels. This is because attention and concentration help to reduce distractions and allow athletes to stay focused on the task at hand.
Environmental Factors Affecting Arousal Levels
Environmental stimuli can significantly impact arousal levels. External factors such as noise, temperature, and social interactions can influence an individual’s physiological and psychological state, affecting their arousal levels.
Noise, both in terms of volume and type, can have a substantial effect on arousal. Moderate levels of noise can enhance arousal, improving performance in certain tasks. However, excessive or unpredictable noise can lead to over-arousal, impairing concentration and decision-making abilities.
Temperature
Temperature also plays a role in arousal levels. Optimal temperatures for peak performance vary depending on the individual and the activity being performed. In general, moderate temperatures tend to promote higher arousal levels, while extreme temperatures can lead to discomfort and reduced performance.
Social Interactions and Competition
Social interactions and competition can significantly influence arousal levels. The presence of others, particularly in competitive situations, can increase arousal and motivation. However, social anxiety or fear of evaluation can lead to under-arousal, hindering performance.
Cultural Factors
Cultural factors can also shape arousal levels. Cultural norms and values influence individuals’ perceptions of situations and their appropriate responses. For example, cultures that emphasize collectivism may promote higher arousal levels in group settings, while individualistic cultures may encourage lower arousal levels in such situations.
Methods for Measuring Arousal Levels: An Athlete’s Arousal Level Refers To
Accurately assessing arousal levels is crucial for understanding and optimizing athletic performance. Various methods have been developed to measure arousal levels, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Physiological Measures
- Heart Rate Monitoring:Measures heart rate variability (HRV), which reflects changes in the autonomic nervous system activity associated with arousal. Higher HRV indicates lower arousal, while lower HRV indicates higher arousal.
- Skin Conductance:Measures the electrical conductance of the skin, which increases with sweat production.
Higher skin conductance indicates higher arousal.
Psychological Measures, An athlete’s arousal level refers to
- Subjective Ratings:Athletes self-report their perceived arousal levels using scales or questionnaires. These measures provide direct insight into the athlete’s subjective experience but may be influenced by biases or social desirability.
- Thought Sampling:Athletes record their thoughts and feelings at specific intervals during a performance.
This method provides real-time insights into the athlete’s cognitive and emotional state.
Environmental Measures
- Ambient Temperature:Extreme temperatures can affect arousal levels, with higher temperatures generally leading to higher arousal.
- Noise Levels:Loud noises can increase arousal, while quiet environments can promote relaxation.
Interpretation of Results
Interpreting arousal level measurements requires consideration of the context and the specific method used. Generally, higher arousal levels may be associated with improved performance in tasks requiring speed and power, while lower arousal levels may be beneficial for tasks requiring precision and focus.
However, the optimal arousal level varies depending on the individual athlete and the specific task.
Applications of Understanding Arousal Levels
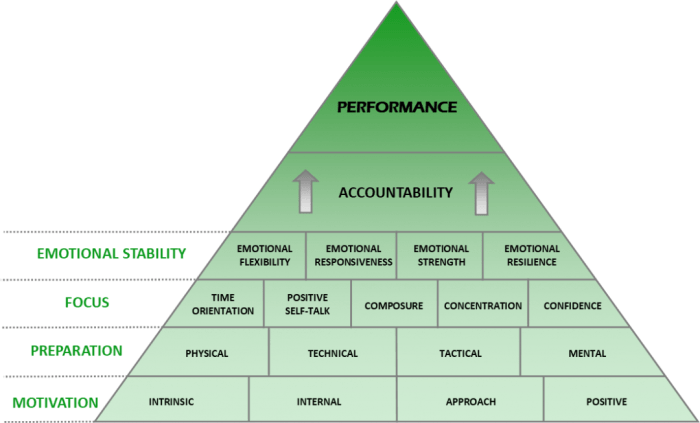
Understanding arousal levels provides athletes with valuable insights to enhance their performance and well-being. By recognizing the optimal arousal zones, athletes can tailor their training and competition strategies to maximize their potential.
Optimizing Performance
Elevated arousal levels can enhance focus, reaction time, and physical strength. Athletes who are sufficiently aroused are more likely to exhibit optimal performance. However, excessive arousal can lead to anxiety, muscle tension, and impaired decision-making. Understanding the relationship between arousal levels and performance allows athletes to find the ideal balance for their specific sport and situation.
Preventing Burnout
Chronic high arousal levels can contribute to burnout, a state of physical and emotional exhaustion. By monitoring their arousal levels, athletes can identify when they are approaching burnout and take steps to prevent it. This may involve adjusting training intensity, seeking relaxation techniques, or consulting with a sports psychologist.
Managing Arousal Levels Effectively
Various techniques can be employed to manage arousal levels effectively. These include:
Cognitive strategies
Athletes can use positive self-talk, visualization, and relaxation techniques to control their arousal levels.
Behavioral strategies
Engaging in calming activities, such as listening to music or taking a warm bath, can help reduce arousal levels. Conversely, engaging in stimulating activities, such as exercise or caffeine consumption, can increase arousal levels.
Physiological strategies
Breathing exercises, such as deep breathing or diaphragmatic breathing, can help regulate arousal levels.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key physiological factors that affect arousal levels?
Hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, as well as the nervous system, play a significant role in regulating arousal levels.
How do psychological factors influence arousal levels?
Motivation, expectations, anxiety, stress, and cognitive processes can all impact arousal levels.
What are some common methods used to measure arousal levels?
Heart rate monitoring, skin conductance, and self-report questionnaires are commonly used methods for measuring arousal levels.